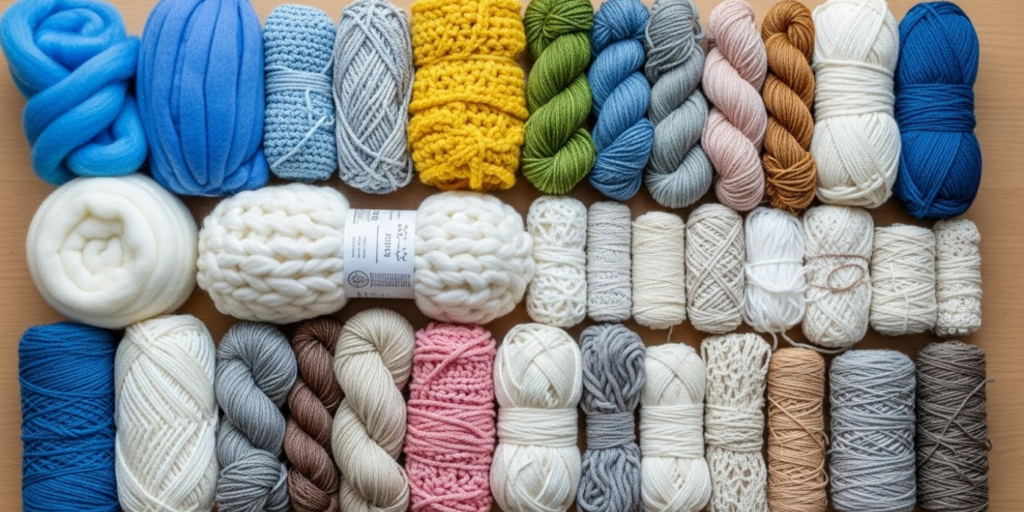
Introduction
Have you ever stopped to wonder why some sweaters feel like a warm hug while others itch like sandpaper? Or why your favorite pair of socks lasts for years, while another unravels after just a few washes? The secret lies not in magic—but in science. More specifically, in the fascinating world of yarn fibers and how their unique properties influence performance, comfort, and durability.
Yarn is far more than just twisted threads—it’s a carefully engineered product shaped by the natural or synthetic characteristics of its fibers. From cozy alpaca blends to high-tech moisture-wicking synthetics, each fiber brings its own set of strengths (and weaknesses) to the table. Understanding these differences empowers crafters, designers, and even everyday consumers to make smarter, more intentional choices.
In this article, we’ll unravel the science behind yarn by exploring the physical and chemical properties of common fibers—both natural and man-made. We’ll examine how these properties affect everything from stitch definition to environmental impact. Along the way, you’ll discover practical tips for selecting the right yarn for your next project, whether you’re knitting a baby blanket, crocheting a market tote, or designing performance activewear. By the end, you’ll see yarn not just as a craft supply—but as a marvel of material science.
Natural Fibers: Nature’s Time-Tested Toolkit
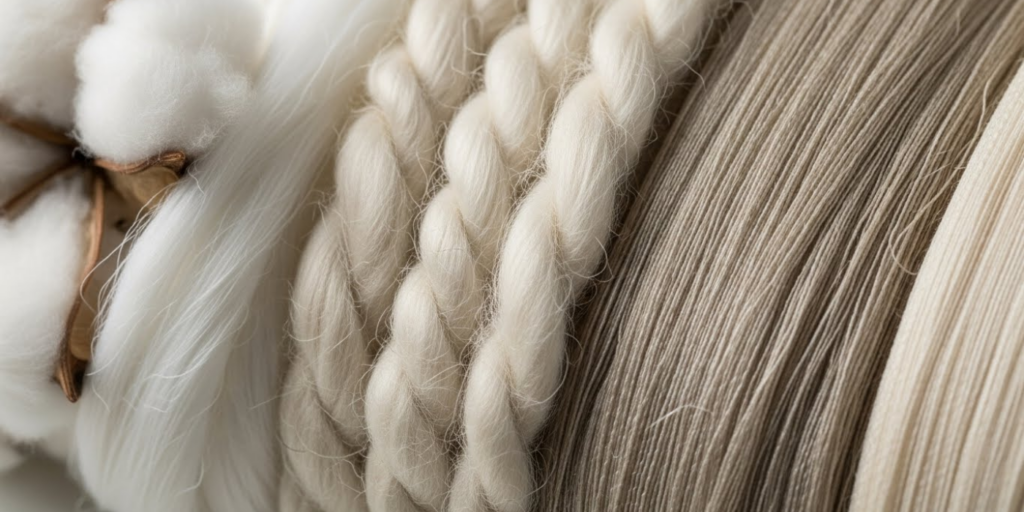

Natural fibers—those derived from plants, animals, or minerals—have been used for millennia. Their enduring popularity isn’t just about tradition; it’s rooted in performance. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common: wool, cotton, linen, and silk.
Wool, harvested primarily from sheep, is celebrated for its elasticity, warmth, and moisture-wicking ability. Its secret weapon? A scaly outer layer and a crimped inner structure that traps air, creating natural insulation. Plus, wool can absorb up to 30% of its weight in moisture without feeling damp—ideal for winter wear or hiking socks. Merino wool, in particular, is prized for its softness and reduced itch factor.
Cotton, a plant-based fiber, offers breathability and absorbency, making it perfect for summer garments and baby items. However, it lacks elasticity, which can lead to sagging in knitted items over time. Mercerized cotton—a treated version—adds luster and strength, improving its performance.
Linen, made from flax, is incredibly strong (even stronger when wet!) and highly breathable. Though initially stiff, it softens beautifully with use. And silk? Luxuriously smooth, with a natural sheen and excellent drape—though it’s less elastic and more delicate than wool.
Understanding these traits helps you match fiber to function. Need a cozy scarf? Wool’s your go-to. Planning baby booties? Soft, hypoallergenic cotton wins. By aligning fiber properties with your project’s needs, you set yourself up for success—and satisfaction.
Synthetic Fibers: Engineered for Modern Demands
While natural fibers have centuries of history behind them, synthetic fibers are the products of 20th-century innovation—and they’ve revolutionized the textile world. Acrylic, nylon, polyester, and spandex may not come from sheep or cotton fields, but they offer unique advantages that natural fibers sometimes can’t match.
Acrylic, for instance, is often used as a wool substitute. It’s lightweight, affordable, and colorfast—meaning it resists fading even after repeated washing. It’s also hypoallergenic, making it a solid choice for people sensitive to animal fibers. However, it’s less breathable and can pill over time.
Nylon shines in durability and elasticity. That’s why it’s commonly blended with other fibers (especially in sock yarns)—it adds strength and helps garments retain their shape. Polyester, another workhorse, offers quick-drying capabilities and excellent wrinkle resistance, making it ideal for activewear or travel clothing.
Then there’s spandex (or elastane), the secret behind stretchy yoga pants and snug beanies. Even in small percentages (as little as 3–5%), it imparts significant stretch and recovery.
One major perk of synthetics? Consistency. Unlike natural fibers, which can vary by season, region, or animal diet, synthetic fibers are engineered for uniform performance. They’re also often more resistant to moths, mildew, and UV rays.
That said, synthetics aren’t without drawbacks. They’re derived from petroleum, raising environmental concerns, and they don’t biodegrade easily. Still, when used thoughtfully—especially in blends—they can dramatically enhance yarn performance.
Pro Tip: Look for blends like “80% merino wool, 20% nylon” for socks—natural comfort with synthetic durability.
Blends: The Best of Both Worlds?
If natural fibers bring soul and synthetics bring science, then blends bring synergy. Most commercial yarns today are blends—and for good reason. By combining fibers, manufacturers can balance strengths and offset weaknesses.
Consider a common blend: cotton and acrylic. Cotton provides softness and breathability, while acrylic adds affordability, elasticity, and color retention. The result? A versatile yarn suitable for everything from dishcloths to lightweight cardigans.
Or take wool and silk—a luxurious pairing. Wool offers warmth and structure; silk contributes sheen, drape, and strength. Together, they create a yarn that’s both cozy and elegant, perfect for shawls or special-occasion garments.
Even eco-conscious blends are emerging. Tencel™ (lyocell), made from sustainably sourced wood pulp, is increasingly blended with cotton or wool to add softness and moisture management with a lower environmental footprint.
But blending isn’t just about performance—it’s also about accessibility. High-end fibers like cashmere or alpaca can be cost-prohibitive on their own. Blending them with more affordable fibers (like merino or acrylic) makes luxury more attainable without sacrificing too much quality.
When choosing a blend, ask yourself: What do I need this yarn to do? Warmth? Drape? Durability? Washability? The right blend can hit multiple targets at once—making your project not only beautiful but functional.
Fiber Properties in Action: How They Affect Your Projects
Now that we’ve explored fiber types, let’s connect the science to your actual crafting experience. How do fiber properties translate into real-world knitting or crocheting results?
Stitch definition, for example, depends heavily on fiber smoothness. A tightly spun silk or mercerized cotton will show off intricate lace or cable patterns beautifully. In contrast, a lofty, fuzzy mohair might blur those details into a soft halo—gorgeous in its own way, but not ideal for complex textures.
Drape—how a fabric flows and hangs—is influenced by fiber weight and flexibility. Silk, bamboo, and fine cotton create fluid, elegant drape, perfect for scarves or summer tops. Wool and acrylic, especially in thicker weights, yield stiffer fabrics better suited for structured items like bags or sweaters.
Then there’s care and maintenance. Wool can felt if agitated in hot water—so hand-washing is often recommended. Cotton, while machine-washable, may shrink or stretch. Synthetics generally tolerate machine washing but can melt under high heat. Always check the care label—and consider your lifestyle. If you hate hand-washing, maybe skip that 100% wool sweater.
Wear and tear matters too. High-abrasion areas (like sock heels or bag handles) benefit from nylon or polyester reinforcement. Baby items need softness and washability—organic cotton or superwash merino are great choices.
By understanding how fiber properties manifest in finished objects, you move from guessing to intentional creation. You’re no longer just following a pattern—you’re engineering a garment that performs exactly as you envision.
Sustainability and the Future of Yarn Science

As crafters become more eco-conscious, the conversation around yarn is expanding beyond aesthetics and performance to include environmental impact. And fiber choice plays a huge role here.
Natural fibers like organic cotton, hemp, and linen are biodegradable and often grown with fewer chemicals. Wool is renewable (sheep grow it back!) and compostable. But conventional cotton farming uses vast amounts of water and pesticides—so certification matters.
Synthetics, while durable, shed microplastics during washing, contributing to ocean pollution. However, innovations are emerging: recycled polyester from plastic bottles, biodegradable nylons, and closed-loop processes like those used in Tencel™ production.
The future of yarn may lie in next-gen bio-based fibers: lab-grown spider silk, algae-based yarns, or even mycelium (mushroom) textiles. These materials promise the performance of synthetics with the sustainability of naturals.
As a consumer, you have power. Choosing GOTS-certified (Global Organic Textile Standard) yarns, supporting brands with transparent sourcing, or simply using up your stash before buying more—all contribute to a healthier planet.
Did You Know? One kilogram of conventional cotton can require up to 20,000 liters of water to grow. Opting for organic or recycled options makes a real difference.
Conclusion: Knit with Knowledge, Create with Confidence
From the crimp of a wool fiber to the molecular chain of nylon, every strand of yarn tells a story of science, nature, and human ingenuity. Understanding fiber properties isn’t just academic—it transforms how you craft, wear, and care for your handmade creations.
We’ve explored the warmth and resilience of natural fibers, the versatility of synthetics, the clever balance of blends, and the real-world impact of your fiber choices. Whether you’re drawn to the earthy simplicity of linen or the high-performance edge of a tech-blend sock yarn, knowledge empowers creativity.
So next time you’re standing in a yarn shop, overwhelmed by options, remember: you’re not just picking a color or weight. You’re selecting a material with a unique personality—one that will shape your project’s look, feel, and lifespan.
Your turn: What’s your favorite fiber to work with—and why? Have you tried any innovative blends lately? Share your thoughts in the comments below! And if you found this guide helpful, don’t forget to share it with a fellow crafter who’s ready to knit with confidence. Because when science meets stitch, magic happens—one loop at a time.

Daniele Ferreira is passionate about the world of crochet, dedicating her time to exploring techniques, creating unique pieces, and sharing her knowledge with beginners and aficionados alike. With attention to detail and creativity, she transforms yarn into true works of art, inspiring others to discover the beauty and joy of this manual art.